Difference Between Decentralised and Distributed Systems

Centralised systems have been a common solution for a very long time, as they are generally easy to use and maintain. However, they have some serious drawbacks. Fortunately, centralised systems are not the only way of getting things done. Decentralised and distributed systems have also been known for quite some time, although their real rise began with the advent of blockchain technology. These terms are often confused, however. Decentralised vs distributed system: what's the difference? And which one is related to blockchain technology? In this article, we'll answer these questions and look at the advantages and disadvantages of each of these systems.
What is the difference between decentralised, distributed and centralised systems?
The main difference between centralised, decentralised, and distributed systems is in how decision-making power, data storage, and processing power are organised and distributed across the system.
The concept of centralised vs decentralised vs distributed network
The difference between centralised and decentralised systems is quite simple and intuitive, but that is not the case for decentralised and distributed ones. One of the first successful attempts to distinguish between the two was made in the 1960s by engineer Paul Baran. His classic illustration is now most often used to explain the differences between these systems.
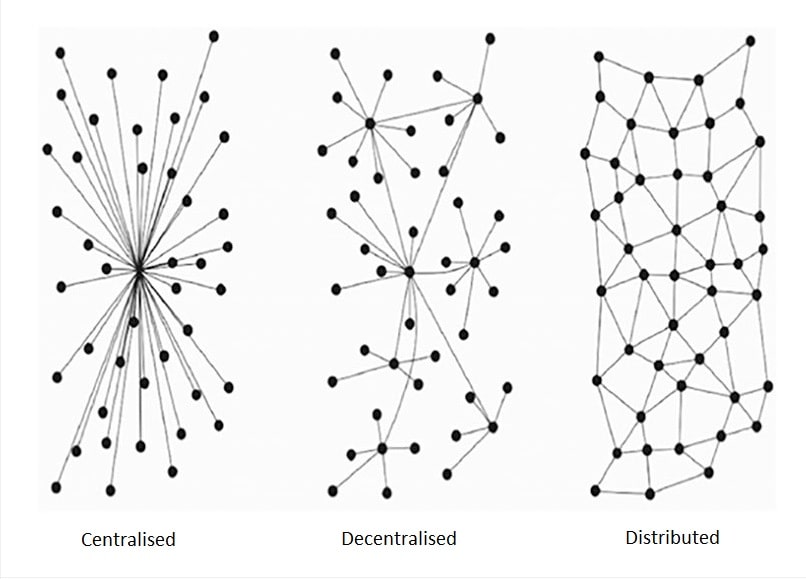
In a centralised system, there is a single point of control, such as a central authority or a single server, that makes decisions and controls access to data and resources. This type of system is highly efficient and easy to manage, but it also has a number of drawbacks, such as susceptibility to censorship as well as vulnerability to attack, downtime and data loss if the central control point is compromised.
What is a decentralised system?
In a decentralised system, decision-making power is distributed among many nodes in the system, with no single point of control. Each participant has equal decision-making power and can verify each other's actions, making the system more transparent and secure.
One prominent example of a decentralised system is blockchain technology, which is used in cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. In a blockchain, all participants have a copy of the ledger and can verify transactions independently. Another example of a decentralised system is a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, which allows users to share resources such as files or bandwidth directly with each other without relying on a central server.
Advantages and disadvantages of decentralised systems
Decentralised systems wouldn't be so famous if they did not have some major advantages over centralised systems:
- Transparency. In a decentralised system, a decision is made across multiple nodes. All these nodes have equal decision-making power and can verify each other's actions. This makes the system more transparent, which helps to build trust.
- Security. Decentralised systems are less vulnerable to attacks and data breaches, as there is no single point of control that can be compromised. The nature of the system means that an attacker would need to compromise multiple nodes simultaneously to successfully attack the system.
- Reliability. Decentralised systems are more reliable than centralised systems, as there is no single point of failure that can bring down the entire system. If one node fails, the system can still continue to function. This makes decentralised systems more resilient to natural disasters, power outages, and other disruptions.
- Resistance to censorship. The lack of a single point of control makes decentralised systems much more resistant to censorship than centralised ones.
However, in addition to the benefits, decentralisation also brings some drawbacks:
- Complexity. Decentralised systems are often more complex than centralised systems, as they require coordination among multiple participants. This can make it more difficult to manage and maintain the system.
- Slower decision-making processes. Decentralised systems typically require consensus among multiple participants, which can lead to slower decision-making processes. This disadvantage can be critical in situations requiring quick decision-making.
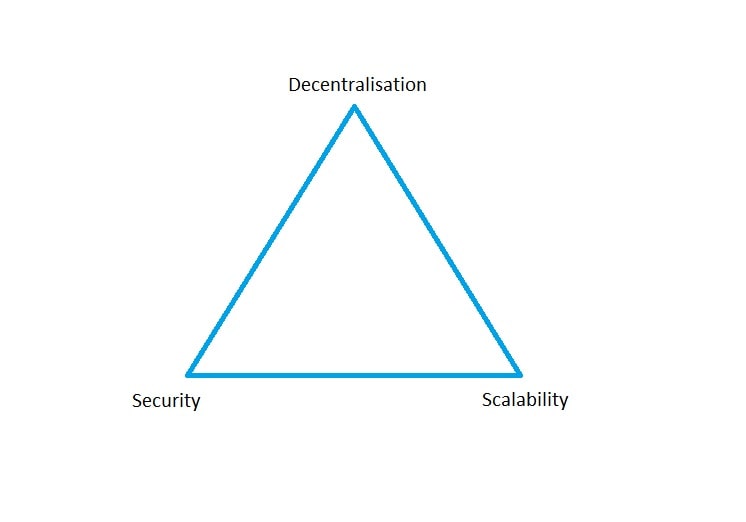
- Scalability challenges. Decentralised systems can be challenging to scale as the system becomes more complex as more participants are added. This shortcoming is reflected in the so-called blockchain trilemma, which refers to the fact that it is very difficult for blockchain to achieve the same high level of decentralisation, scalability and security at the same time.
What is a distributed system?
In a distributed system, data and processing power are spread across all the participants, and each of them can perform processing and decision-making functions independently. Nodes work together to achieve a common goal, such as processing data or delivering content.
One example of a distributed system is a content delivery network (CDN), which distributes content across multiple servers located around the world. Another example of a distributed system is a cluster of servers, which can distribute processing power across multiple nodes to handle large workloads.
Advantages and disadvantages of distributed systems
Distributed systems and decentralised systems share some similarities in terms of their advantages and disadvantages, as both approaches are designed to distribute computing resources across multiple nodes. However, there are some advantages and disadvantages of distributed systems that may not be present in decentralised systems.
Advantages of distributed systems:
- Improved fault tolerance. Distributed systems are usually more fault-tolerant than decentralised systems.
- Increased scalability. Distributed systems are typically more scalable than decentralised systems, as they can be designed to handle larger volumes of data and traffic.
- Higher performance. Distributed systems can offer higher performance than decentralised systems, as data processing can be distributed across multiple nodes.
Disadvantages of distributed systems:
- Higher complexity. Distributed systems are typically more complex than decentralised systems, as they require greater coordination and management across multiple nodes. This complexity can make it more difficult to develop, test, and maintain distributed systems.
- Higher cost. Distributed systems are generally more expensive to implement and maintain than decentralised systems, as they require more hardware, software, and network infrastructure.
Difference between distributed and decentralised systems
Decentralised and distributed systems offer alternative solutions to the limitations of centralised systems. While these systems share some similarities, they also have differences between them. In a distributed system, the workload is shared, unlike in a decentralised system where each node can act as a master server of its own. In a decentralised system, all participants have equal power, and decisions are made by consensus among all participants. In a distributed system, there can be a hierarchy of nodes, with some nodes responsible for coordinating the actions of others.
Are blockchains decentralised or distributed systems?
Blockchains are often referred to as both decentralised and distributed systems. The decentralised aspect of a blockchain refers to the fact that there is no central authority or single point of control. Instead, all participants in the network have equal decision-making power, and decisions are made by consensus through a series of rules and protocols. However, this doesn't apply to all blockchain networks. Depending on the design of a particular blockchain network, it can either be decentralised or centralised.
The distributed aspect of a blockchain refers to the fact that data and processing power are spread across a network of nodes. Each node has a copy of the blockchain and works together with other nodes to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. This distribution of data and processing power makes blockchains more secure and resistant to attacks, as there is no single point of failure that can be exploited.
Tags
Try our Bitcoin Cloud Miner and get additional crypto rewards based on your trading volume. It's immediately available upon registration.
Try our Bitcoin Cloud Miner and get additional crypto rewards based on your trading volume. It's immediately available upon registration.



