The difference between public key and private key cryptography

The key element of any blockchain project is the cryptography used to protect data. Without it, no transactions are protected. The cryptocurrencies we all know are built on so-called public key cryptography. In this article, we'll look at the difference between public key cryptography and private key cryptography with examples, discuss each system's advantages and disadvantages, and answer other questions on this topic.
What are public and private key cryptography?
Let's begin our discussion by learning the difference between public key cryptography and private key cryptography.
There are two basic concepts in cryptography: encryption and decryption. Encryption is the transformation of the original message into an unreadable, i.e., encrypted one. Decryption is the conversion of an encrypted message back to its original form. An algorithm and key are used for both encryption and decryption, and there are two methods of encryption and decryption: symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption, also called private key encryption, has been known to humanity for a very long time. On the other hand, asymmetric encryption, also called public key encryption, appeared only in the 1970s and became really widespread as the Internet developed.

Now that you know the basics, let's move to the difference between public key cryptography and private key cryptography.
What is private key encryption?
Private key encryption is a very popular, simple and effective encryption system. It allows both encryption and decryption to be performed using the same key. Since anyone who has the key can decrypt information encrypted in this way, this key must be kept secret and accessible only to the sender and the recipient of the information. This is why it's called a private key, and the encryption system itself is called private key encryption.
What is public key encryption?
This encryption system is much more complex, using the private key only to decrypt the message. To encrypt the same message, a separate public key derived from the public key is used. If a person knows the private key, they can calculate the public key. However, knowing only the public key isn't enough to calculate the private key. That's why the public key doesn't need to be kept secret since the simple fact of knowing it doesn't allow encrypted information to be decrypted.
Choose your wallet on StormGain
How does public and private key encryption work?
In private key cryptography, the sender encrypts the message using the private key and sends it to the recipient. For the recipient to decrypt the message, they'll need the sender to provide the same private key through a well-secured channel, thus reducing the security of such cryptographic systems.
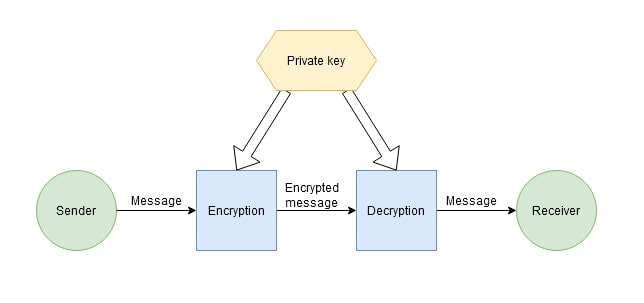
In public key cryptography, the message sender encrypts the message with the public key and sends it to a recipient. The message recipient receives it and decrypts it with the private key that only he or she has. Since only the recipient needs a private key in this encryption system, it doesn't have to be sent, thus increasing its security. In public key cryptography, only the recipient — not even the sender — can decrypt the message.
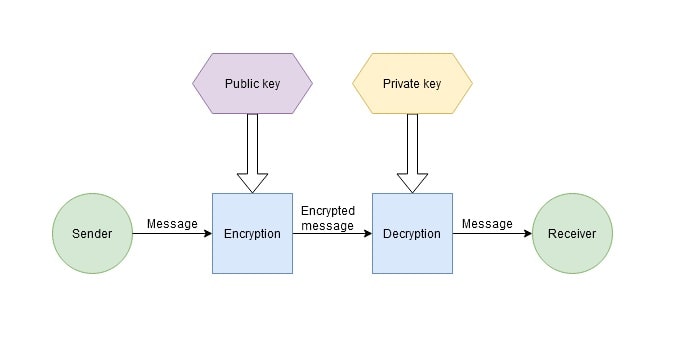
The advantages and disadvantages of public key cryptography
Let's see the advantages and disadvantages of these encryption systems by comparing them to see the difference between public key cryptography and private key cryptography.
Comparison of private and public key cryptography
Private key cryptography | Public key cryptography | |
Encryption-decryption speed | Faster | Slower |
Required computing power | Less | More |
Need to send a private key via a secure channel | Yes | No |
Key length | Shorter | Longer |
Parties who need to know the private key | Recipients and senders | Recipients only |
Complexity of key management in a large network | High | Low |
Able to be used to generate an electronic digital signature | No | Yes |
In this comparison, we see that although private key encryption is much simpler and faster, it's not a suitable option for blockchain networks.
Tags
Try our Bitcoin Cloud Miner and get additional crypto rewards based on your trading volume. It's immediately available upon registration.
Try our Bitcoin Cloud Miner and get additional crypto rewards based on your trading volume. It's immediately available upon registration.
FAQ
What is public key and private key in cryptography?
Let's get public key and private key explained to understand the difference between public key and private key in cryptography:
- Public key cryptography involves the encryption or signing of data using two distinct keys, one of which is the public key, made accessible to anyone. Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, hence asymmetric cryptography. This method is widely utilised, particularly for TLS/SSL, enabling HTTPS.
- On the other hand, the private key, also known as the secret key, is symmetric and used for encryption and decryption. It remains confidential and operates by copying or sharing the same key with another party to decrypt the cypher text, resulting in faster processing than public-key cryptography.
How do public and private keys work?
Public and private keys are integral to public key cryptography, also known as asymmetric encryption. Here's a simplified breakdown of how public and private key encryption work:
- Public Key is used to encrypt data and can be openly distributed for anyone to use in encryption. Once data is encrypted using a public key, it cannot be decrypted using the same key. Complex asymmetric encryption algorithms are used to generate the public key.
- Private Key is employed to decrypt data that has been encrypted with the corresponding public key. It is kept confidential; only the private key owner can decrypt the data.
How can I ensure the security of my private key?
Here are some best practices to ensure the security of your private key:
- Generate keys in a secure environment. If you have shell access to the server where the keys are used, generating them on the spot is best. This way, you avoid the need to transmit them at all.
- Avoid transmitting private keys. As a general rule, private keys should not be transmitted. They cannot be used for their intended purpose if they are not private to one entity.
- Use secure storage. Store your private keys in a secure and encrypted storage solution. This could be a secure server, a hardware security module, or physically secure offline storage.
- Use strong passwords: If your private key is password-protected (which it should be), use a strong, unique password.
- Regularly update and rotate keys. It's important to regularly update and rotate your keys to reduce the risk if a key is compromised.
- Use Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). If you need to transmit a private key, use a public key infrastructure. The receiving party generates a public/private key pair. The sending party will then use the receiving party's public key to encrypt the private key and send it.
Why is the private key crucial in cryptography?
The private key is essential in cryptography for several key reasons:
- Security and Integrity of Transactions. Private key cryptography is essential for ensuring the security of transactions and ownership of digital assets within a blockchain. Each participant has a unique private key to sign transactions, generating a digital signature to authenticate the transaction. Only the rightful owner can transfer an asset, preventing unauthorised access.
- Secure Proof of Ownership. Without private key encryption, there is no secure way to prove digital asset ownership or verify transaction authenticity. This could result in fraudulent transactions and compromise the integrity of the entire blockchain system.
- Anonymity of Transactions. Private key cryptography also provides anonymity for blockchain transactions, enhancing privacy and security.
- Confidentiality of Encrypted Information. The private key is crucial for ensuring the security and confidentiality of encrypted information in private key cryptography.



