What is Proof of Work?

For a better understanding of Proof-of-Work and how it works, let's refer to the fundamentals of blockchain technology first.
One of the main properties of blockchain technology, the basis of cryptocurrencies, is decentralisation. This means that all nodes in the blockchain network are equal, and there's no central authority to decide which transactions are valid and which aren't. But how, then, do the network participants solve this issue? They need to reach a consensus. This is done using a mechanism called a consensus algorithm.
A consensus algorithm is a set of mathematical rules that allow nodes in the network to agree while eliminating invalid and fraudulent transactions. The oldest and most well-known consensus algorithm used in cryptocurrencies is Proof of Work.
In this article, we'll explainProof of Work, how it ensures the blockchain functions properly, what advantages and disadvantages it has, "what is proof of work and proof of stake?" and what alternatives to Proof of Work exist.
The proof-of-work also solves the problem of determining representation in majority decision-making. If the majority were based on one-IP-address-one-vote, it could be subverted by anyone able to allocate many IPs. Proof-of-work is essentially one-CPU-one-vote. — Satoshi Nakamoto.
Proof of Work explained
What is a Proof-of-Work algorithm? Proof of Work (PoW) is a consensus algorithm that makes the blockchain network nodes do very complex computational work (algorithm calculation) to confirm transactions.
How does Proof-of-Work work? Other network nodes can easily and quickly verify their result. The first node to successfully complete all the required computations receives a reward from the blockchain network. Because of this, nodes compete for the opportunity to become the first and receive the reward.
Although the Proof of Work in blockchain currently has a strong association with cryptocurrencies, an algorithm similar to it was initially proposed in 1993 in a scientific work devoted to combating spam. The term "Proof of Work'' itself first appeared in 1999. However, it was only with the advent of Bitcoin and the beginning of the cryptocurrency era that this algorithm found widespread practical application.
How the Proof of Work algorithm works
Proof of Work in blockchainlets miners verify transactions and create new blocks. To reward miners for their work, the network must establish rules to select a miner who will have the right to generate the next block in the chain.
Here's how the algorithm works:
- Blockchain network users form transactions by sending cryptocurrency to each other.
- Transactions are combined into blocks.
- Miners verify the validity of transactions within blocks.
- The miners then solve a complex mathematical puzzle by calculating the correct hash for the block. Those calculations require a lot of computing power.
- A reward is given to the first miner to solve the puzzle.
- The blocks with verified transactions are stored on the blockchain.
Advantages and disadvantages of Proof of Work
Proof of work effectively protects the blockchain network from hacking attempts by making them very difficult and costly. Moreover, the more miners work in the network, the more resistant the network becomes to hacking attempts. In addition, this consensus algorithm is the oldest and most tested through practice.

Nevertheless, PoW in crypto also has some notable drawbacks that led to the development of alternative consensus algorithms.
- High electricity consumption and useless computing. Miners consume huge amounts of electricity, but the calculations they make don't go anywhere except for the network's needs.
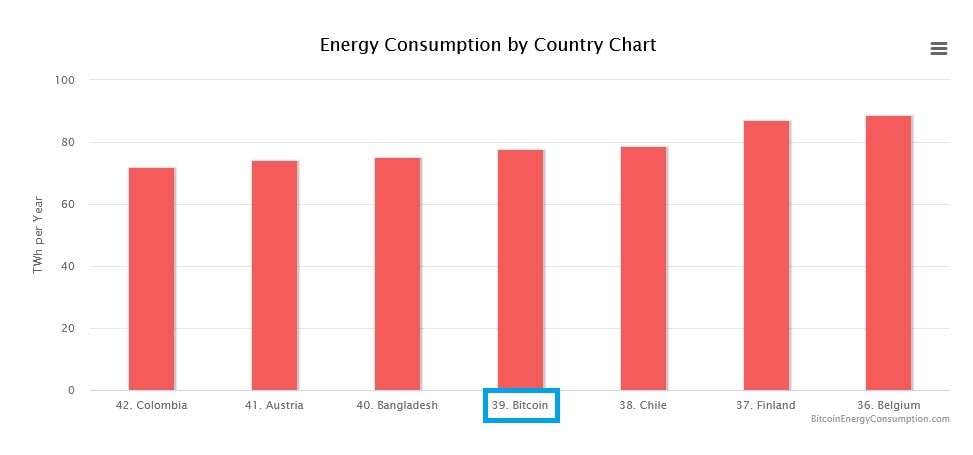
- Significant computing power is required to keep the Proof of Work blockchain working. For example, you can't mine Bitcoin on cheap video cards; it requires powerful, expensive, specialised equipment known as ASICs, which aren't suitable for performing any other tasks.
- As the network and the calculations become more complex, the cost of mining equipment ceases to be affordable to ordinary users. Only large communities of miners or wealthy people and companies with powerful mining farms can mine blocks and confirm transactions. This increases centralisation as owners of large mining capacities begin to dictate the rules of the network.
- Vulnerability to a 51% attack. If an attacker controls more than 50% of the network hash rate, they can tamper with, cancel or change transactions for their own purposes. Likewise, they can perform other malicious actions with the blockchain. Since the hacker's hashing power is higher than the rest of the network's in this scenario, the hacker's chain version will be accepted. While attacks like these are difficult to carry out for popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin due to the very high hash rate, the threat is very real for less popular cryptocurrencies.
Advantages and disadvantages of the Proof of Work algorithm
Advantages | Disadvantages |
High level of protection against hacking attempts | High energy consumption |
It's the oldest and most time-honoured of all consensus algorithms | The need for huge computing power |
Increase in network centralisation | |
Vulnerability of blockchain to 51% attack |
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
Due to the problems mentioned above, the blockchain industry is trying to develop alternatives to Proof of Work, the first of which was the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. Proposed in 2011, it was first used in the Peercoin cryptocurrency.
What's the difference between Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake? Unlike Proof of Work, Proof of Stake doesn't require any calculations. Those who wish to add a block and receive a reward are selected randomly from among the users who have reserved ("staked") a certain amount of the respective cryptocurrency for this purpose. The probability of being selected depends on the stake's size and other indicators, such as the stake's age. You can learn more about the Proof of Stake algorithm in our article on the topic.
With its features, the Proof of Stake algorithm solves the major problems inherent in Proof of Work. Thanks to the lack of computation, the Proof of Stake blockchain doesn't require expensive mining equipment or large amounts of electricity to function, which, in turn, prevents centralisation. A hacker would need to accumulate more than 50% of a cryptocurrency to carry out a 51% attack, making it pointless since they would incur the greatest losses.
Is Proof of Stake better than Proof-of-Work? Proof of Stake has its own drawbacks. The relation of the chance of getting a reward to the size of the stake incentivises users to accumulate coins instead of using them for payments. Also, a small group of major coin holders may dictate their rules to the entire network. Moreover, cryptocurrency developers based on this algorithm have to solve the initial coin distribution problem since, to stake coins, they must first be obtained from somewhere.
Cryptocurrencies that use Proof of Work
Proof of Work is currently one of the most common consensus algorithms for cryptocurrencies. Consider the following Proof-of-Work coin list.
Bitcoin and Proof of Work
Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, was also the first practical implementation of the Proof of Work algorithm in the blockchain industry. In the Bitcoin protocol, the Proof of Work is based on the SHA-256 hashing algorithm. The mining difficulty adjusts after every 2016th block. The average block generation time is 10 minutes.
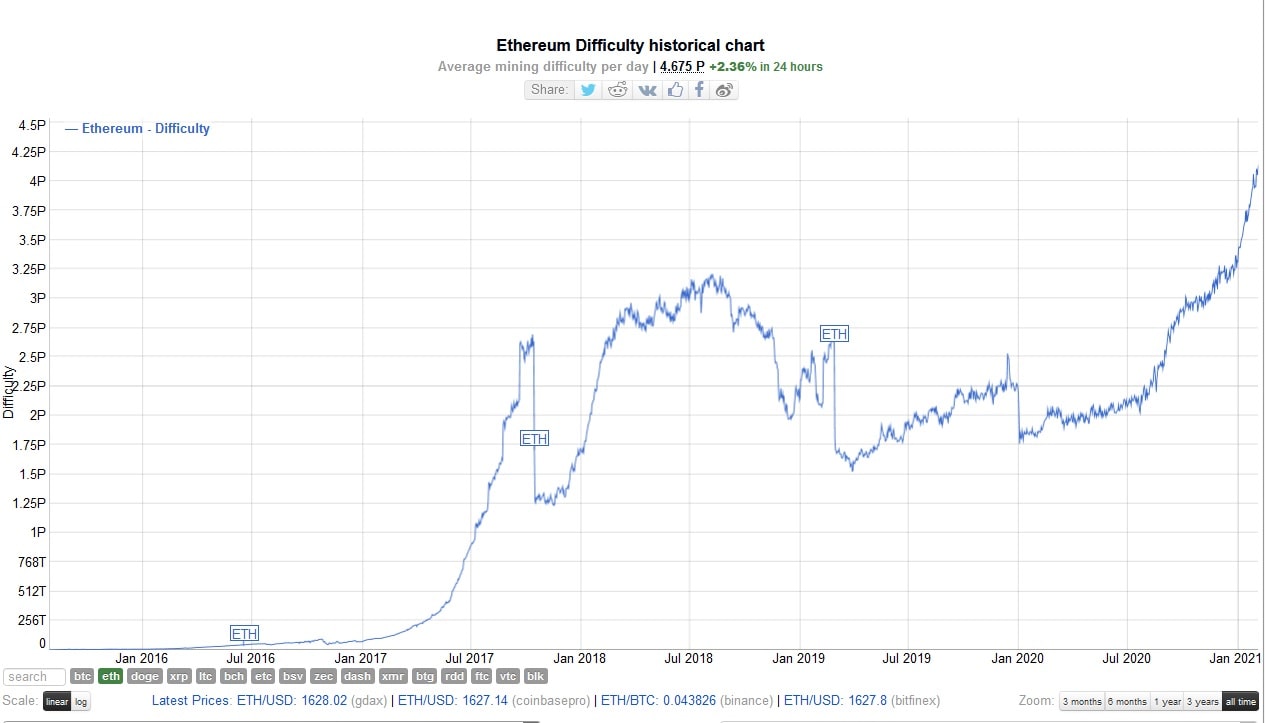
Ethereum and Proof of Work
Vitalik Buterin, the developer of Ethereum, originally wanted to use the Proof of Stake algorithm, but due to its inherent problems, he was forced to use the more tried and tested Proof of Work algorithm. Despite this, he planned to completely abandon PoW and switch to PoS as soon as these problems were solved. Although the lengthy transition process has been postponed many times, it is now underway. However, the completion date is still unknown.
In the Ethereum protocol, the Proof of Work algorithm is based on the Ethash hashing algorithm. The average block generation time is 13 seconds.
Other Proof of Work altcoins
It's impossible to add the entire Proof-of-Work list of cryptos to this article, so we'll keep it to only the most notable ones.
Cryptocurrencies with PoW consensus algorithm
Name | Description |
Litecoin (LTC) | An analogue of Bitcoin with faster and cheaper transactions |
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) | A Bitcoin fork with increased block size and reduced time between difficulty adjustments |
Monero (XMR) | A cryptocurrency with increased anonymity based on the CryptoNight hashing algorithm |
Ethereum Classic (ETC) | An Ethereum hard fork |
Binance Coin (BNB) | The token of the Binance crypto exchange |
Dogecoin (DOGE) | A cryptocurrency for small payments with fast and cheap transactions. Originally created as a joke |
ZCash (ZEC) | An anonymous cryptocurrency |
Bitcoin Gold (BTG) | An ASIC-resistant Bitcoin fork with increased decentralisation |
Verge (XVG) | An anonymous cryptocurrency. Supports several hashing algorithms. Based on the Bitcoin blockchain |
Cryptocurrencies without the Proof of Work algorithm
The inherent drawbacks of the PoW algorithm encourage blockchain developers to look for alternatives. In addition to the previously mentioned Proof of Stake, many alternative consensus algorithms have been developed. Here are the most popular ones.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus algorithm in which the right to confirm blocks is delegated to a group of people elected by voting. The weight of the network participants' votes depends on the number of coins in their possession. It's used in EOS (EOS) and Lisk (LSK).

- Proof of Activity is a mixed approach that combines Proof of Work and Proof of Stake algorithms. An example of using this algorithm is Esper (ESP).
- Proof of Capacity is a consensus algorithm based on using free disk space on hard drives to place solutions to a cryptographic problem. This means that the chance of successfully generating a block is proportional to the volume of allocated disk space. It's used in Storj (STORJ) and Burst (BURST).
- Proof of Burn is a consensus algorithm based on the principle of "burning" coins. With this algorithm, miners send coins to an address from which it is impossible to withdraw them. By doing this, miners get a constant chance to generate a block and receive a reward. The likelihood of this happening increases in proportion to the number of coins burned. Such an algorithm is not very good at the initial stage of cryptocurrency development, but it can be effective at later stages. Proof of Burn is used in Slimcoin (SLM) and Counterparty (XCP).
Tags
Try our Bitcoin Cloud Miner and get additional crypto rewards based on your trading volume. It's immediately available upon registration.
Try our Bitcoin Cloud Miner and get additional crypto rewards based on your trading volume. It's immediately available upon registration.
FAQ
What is PoW in cryptocurrency?
Proof-of-Work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism in numerous cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin. Satoshi Nakamoto introduced Proof-of-Work in crypto in the 2008 Bitcoin whitepaper. PoW necessitates network members exert effort in solving a random mathematical puzzle to prevent system manipulation. This process is often likened to gold mining as it requires substantial effort before transactions are deemed valid.
Here's how it operates:
- Every 10 minutes, a new block of transactions is added to the blockchain ledger for validation.
- Consensus is achieved only when a unique cryptographic equation has been solved.
- Anyone can attempt to solve the equation, but advanced hardware is required.
- The block of transactions gets added to the blockchain upon solving the equation.
- The successful 'miner' receives a reward for solving that specific block
- Subsequently, another block of transactions gets added, offering miners another opportunity.
This process guarantees that only genuine transactions are verified and included on the blockchain, effectively preventing double spending, such as with bitcoins.
However, due to its complex nature, PoW consumes significant energy, which has attracted criticism and prompted alternatives like Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
Why is PoW better than PoS?
Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are consensus mechanisms utilised in blockchain networks to validate transactions. Each method possesses unique strengths and weaknesses, with the choice between them often hinging on the specific use case of the blockchain. Some individuals may favour PoW over PoS due to several reasons:
- Decentralisation: PoW is perceived as more decentralised than PoS since it allows anyone with suitable hardware to engage in the mining process. PoS necessitates users to hold a specific amount of cryptocurrency to become validators.
- Security: The security level of PoW is highly regarded. For a 51% attack on a PoW network, an attacker would need control over more than half of the total computational power, which is typically challenging and costly.
- Proven Track Record: With its longer existence and extensive real-world testing, PoW has established itself as Bitcoin's original consensus mechanism - the first and most prominent cryptocurrency.
The major difference between Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake is that PoS is generally more energy-efficient, providing faster and more scalable transactions.
Moreover, Ethereum's plans to switch from PoW toward PoS depict growing industry trends toward a proof-of-stake model.
Which cryptos are Proof-of-Work?
You'll get a better understanding of Proof-of-Work while checking out the following Proof-of-Work coin list.



